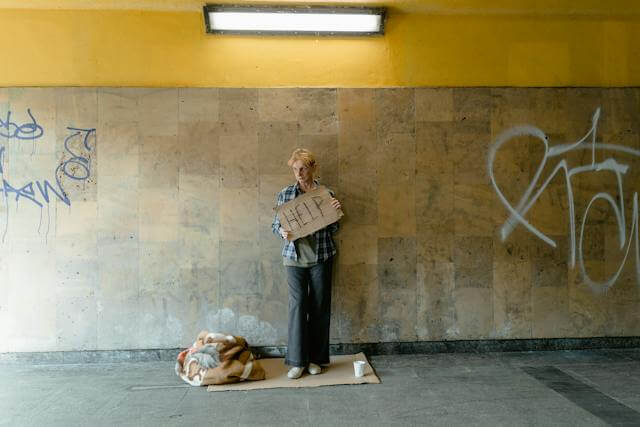
The aging population is a demographic trend that has significant implications for societies around the world. Among the elderly, a specific group that often faces unique challenges is poor senior adults. In this article, we will explore key statistics related to the financial, healthcare, and social aspects of their lives, shedding light on the struggles that many seniors in low-income brackets experience.
Demographic Trends in the Aging Population
As life expectancy increases globally, the proportion of elderly individuals in the population continues to rise. According to recent demographic studies, the number of people aged 65 and above is expected to double by 2050, reaching nearly 1.5 billion. This demographic shift poses various challenges, especially for those living on limited incomes.
Income and Financial Statistics
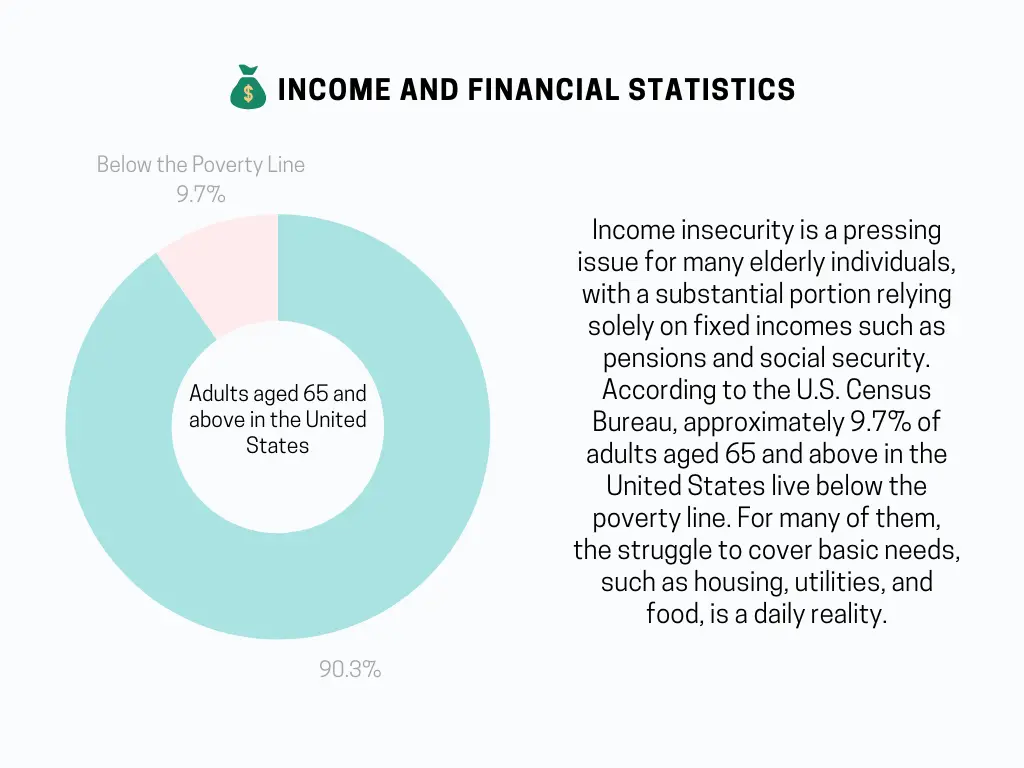
Income insecurity is a pressing issue for many elderly individuals, with a substantial portion relying solely on fixed incomes such as pensions and social security. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, approximately 9.7% of adults aged 65 and above in the United States live below the poverty line. For many of them, the struggle to cover basic needs, such as housing, utilities, and food, is a daily reality.
Healthcare Statistics
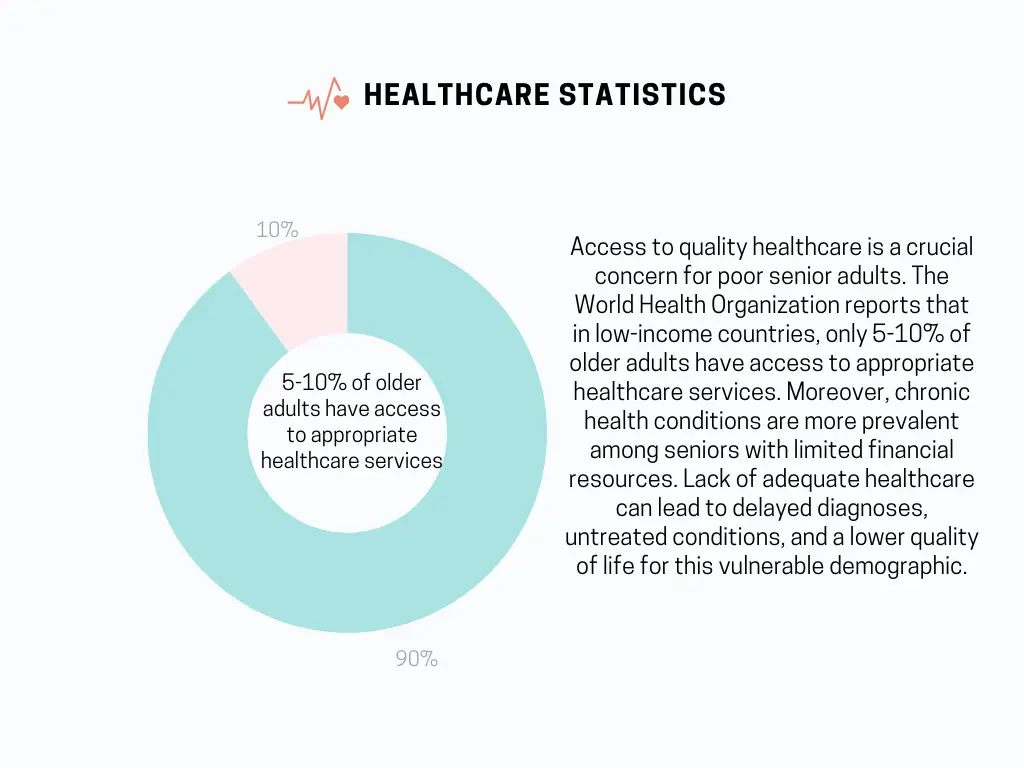
Access to quality healthcare is a crucial concern for poor senior adults. The World Health Organization reports that in low-income countries, only 5-10% of older adults have access to appropriate healthcare services. Moreover, chronic health conditions are more prevalent among seniors with limited financial resources. Lack of adequate healthcare can lead to delayed diagnoses, untreated conditions, and a lower quality of life for this vulnerable demographic.
Social Isolation and Mental Health Statistics
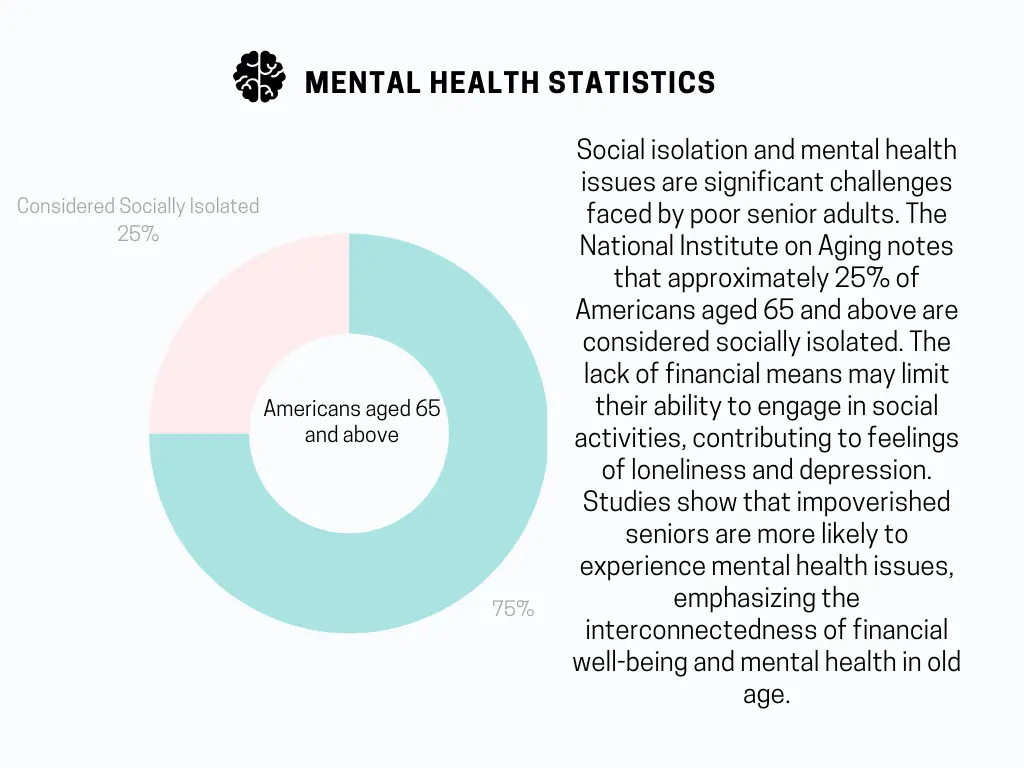
Social isolation and mental health issues are significant challenges faced by poor senior adults. The National Institute on Aging notes that approximately 25% of Americans aged 65 and above are considered socially isolated. The lack of financial means may limit their ability to engage in social activities, contributing to feelings of loneliness and depression. Studies show that impoverished seniors are more likely to experience mental health issues, emphasizing the interconnectedness of financial well-being and mental health in old age.
Conclusion
Understanding the statistics related to poor senior adults is crucial for developing targeted interventions and support systems. As the global population continues to age, it is imperative to address the financial, healthcare, and social challenges faced by this vulnerable demographic. Policymakers, healthcare professionals, and communities must work collaboratively to ensure that elderly individuals in low-income brackets receive the care, support, and resources they need to age with dignity and security.

Morgan Elfman is a compassionate writer, dedicated caregiver, and passionate advocate for senior well-being. Born and raised with a deep sense of empathy and a natural inclination towards service, Morgan has devoted her life to making a positive impact on the lives of seniors.
As a writer for www.choiceseniorlife.com, Morgan utilizes his skills to create insightful and informative content that addresses the unique needs and challenges faced by seniors and their families. Her articles not only provide valuable information on health, lifestyle, and care options but also strive to inspire and empower seniors to lead fulfilling lives.

