The inevitability of death is a reality that we all face, but its impact is felt most poignantly among our senior citizens. Each year, a significant number of the elderly pass away, leaving behind a wealth of history, wisdom, and connections. It’s not just about the numbers; it’s about understanding the stories behind these statistics and the societal implications they hold.
Statistics On Number of Senior Citizens Who Die Each Year
According to the latest data from the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 6.7 million people aged 70 years and over died globally in 2021. This statistic, while stark, is more than just a figure; it represents a diverse group of individuals, each with their own unique life experiences.
Breaking Down the Statistics
The mortality rate among seniors varies significantly across different regions and is influenced by a range of factors, including healthcare quality, lifestyle choices, and socioeconomic status. In developed countries, where access to quality healthcare is generally higher, the mortality rate is often lower compared to developing countries.
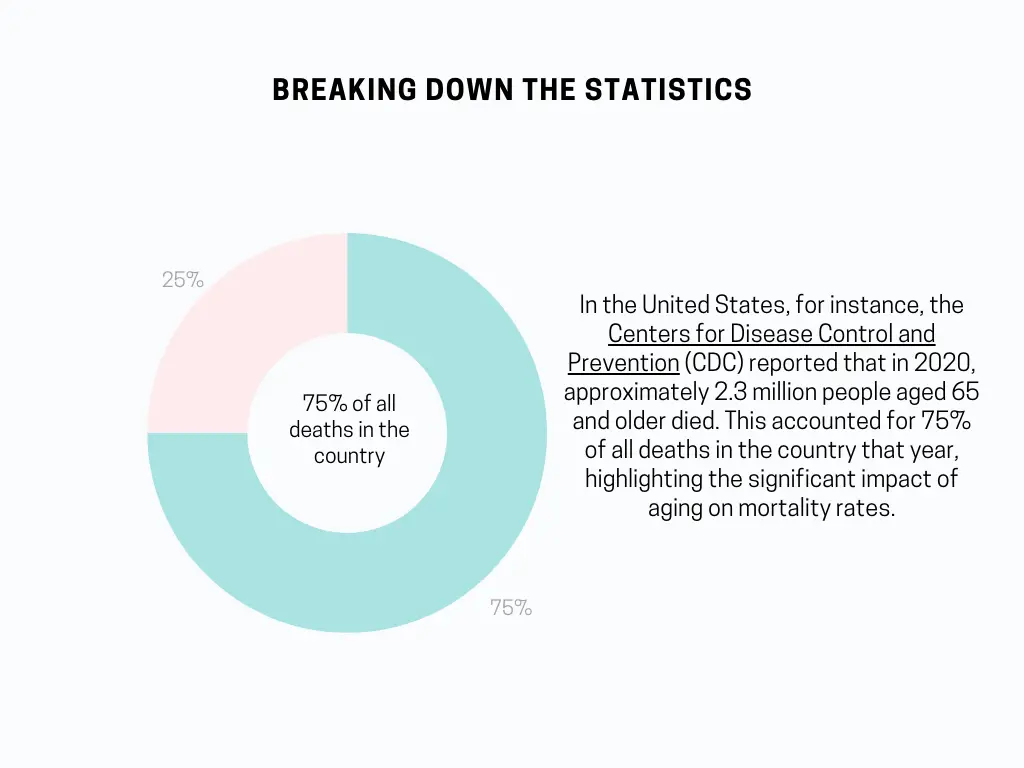
In the United States, for instance, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported that in 2020, approximately 2.3 million people aged 65 and older died. This accounted for 75% of all deaths in the country that year, highlighting the significant impact of aging on mortality rates.
The Role of Chronic Diseases
Chronic diseases play a substantial role in the mortality of senior citizens. Conditions such as heart disease, cancer, chronic lower respiratory diseases, and stroke top the list of causes. The CDC notes that heart disease alone was responsible for about 696,962 deaths among seniors in 2020.
These numbers reflect the importance of preventative health measures and the need for improved healthcare services targeting the elderly, especially in managing and treating chronic conditions.
Life Expectancy and Gender Differences
Life expectancy plays a crucial role in understanding these statistics. Globally, the average life expectancy has been increasing, thanks to advancements in medicine and healthcare. However, there is a noticeable difference between genders. Women generally live longer than men, a trend seen in most countries around the world. This gender disparity in life expectancy also influences the overall mortality figures for senior citizens.
Social and Economic Implications
The death of senior citizens has profound social and economic implications. The loss of the elderly means a loss of history, tradition, and experience. They often play key roles in families and communities, acting as caretakers, advisors, and connectors of generations.
From an economic perspective, the passing of seniors can impact workforce dynamics, pension systems, and healthcare expenditures. As the global population ages, these issues are becoming increasingly important for policymakers to address.
Looking Ahead
The statistics on senior citizen mortality are more than just numbers; they represent real lives and real stories. They highlight the need for improved healthcare, better management of chronic diseases, and greater support for the elderly.
As we look to the future, it’s essential to not only focus on increasing life expectancy but also on improving the quality of life for our seniors. By doing so, we honor their contributions and ensure they remain active, engaged, and valued members of our societies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the mortality rates among senior citizens are a reflection of broader societal health and well-being. By understanding and addressing the factors behind these numbers, we can create a world that respects, values and cares for its eldest members.

Morgan Elfman is a compassionate writer, dedicated caregiver, and passionate advocate for senior well-being. Born and raised with a deep sense of empathy and a natural inclination towards service, Morgan has devoted her life to making a positive impact on the lives of seniors.
As a writer for www.choiceseniorlife.com, Morgan utilizes his skills to create insightful and informative content that addresses the unique needs and challenges faced by seniors and their families. Her articles not only provide valuable information on health, lifestyle, and care options but also strive to inspire and empower seniors to lead fulfilling lives.
